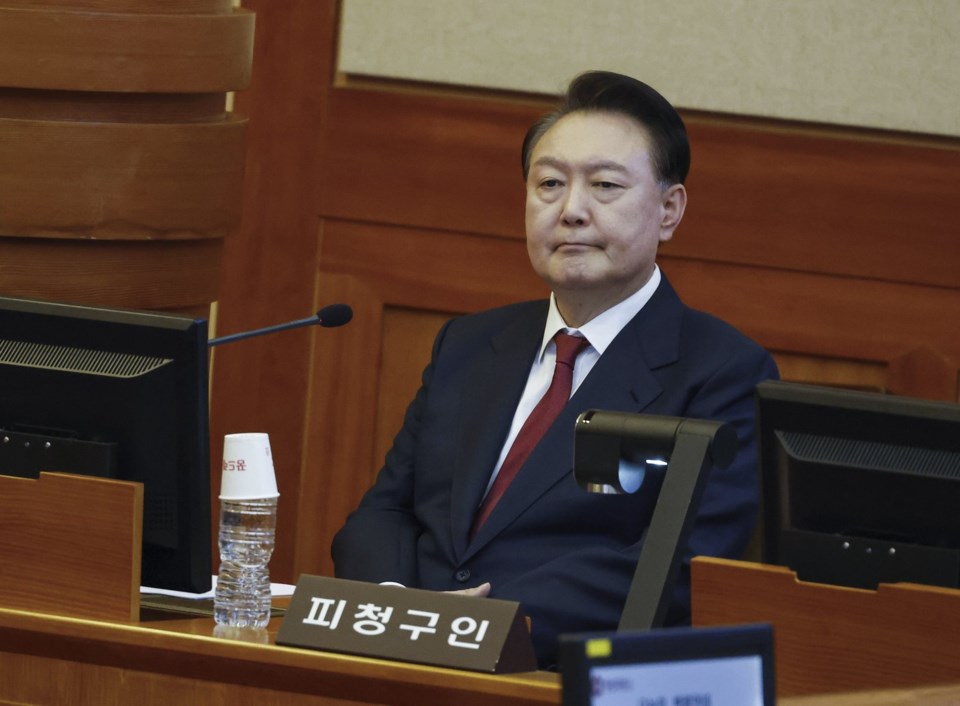
SEOUL, South Korea (AP) — South Korean prosecutors on Sunday indicted impeached President Yoon Suk Yeol on rebellion in connection with his short-lived imposition of martial law, news reports said, a criminal charges that could put him to death or jail for life if convicted.
This is the latest blow to Yoon, who was impeached and arrested over his Dec. 3 martial law decree that plunged the country into huge political turmoil, shaking South Korean politics and financial markets as well as its international image. Separate from criminal judicial proceedings, the Constitutional Court is now deliberating whether to formally dismiss Yoon as president or reinstate him.
South Korean media outlets, including Yonhap news agency, reported that the Seoul Central District Prosecutors’ Office indicted Yoon over rebellion. Calls to the prosecutors’ office and Yoon's lawyers went unanswered.
Yoon, a conservative, has steadfastly denied any wrongdoing, calling his martial law a legitimate act of governance meant to raise public awareness of the danger of the liberal-controlled National Assembly which obstructed his agenda and impeached top officials. During his announcement of martial law, Yoon called the assembly “a den of criminals” and vowed to eliminate “shameless North Korea followers and anti-state forces.”
After declaring martial law on Dec. 3, Yoon sent troops and police officers to the assembly, but enough lawmakers still managed to enter an assembly chamber to vote down Yoon’s decree unanimously, forcing his Cabinet to lift it.
The martial law imposition, the first of its kind in South Korea in more than 40 years, lasted only six hours. However, it evoked painful memories of past dictatorial rules in the 1960s-80s when military-backed rulers used martial laws and emergency decrees to suppress opponents.
South Korea’s constitution gives the president the power to declare martial law to keep order in wartime and other comparable emergency states, but many experts say the country wasn’t under such conditions when Yoon declared martial law.
Yoon insists he had no intentions of disrupting assembly work i ncluding its floor vote on his decree and that the dispatch of troops and police forces was meant to maintain order. But commanders of military units sent to the assembly have told assembly hearings or investigators that Yoon ordered them to drag out lawmakers.
Investigations on Yoon have intensified the country’s already serious internal division, with rival protesters regularly staging rallies in downtown Seoul.
After a local court on Jan. 19 approved a formal arrest warrant to extend Yoon’s detainment, dozens of his supporters stormed the court building, destroying windows, doors and other property. They also attacked police officers with bricks, steel pipes and other objects. The violence left 17 police officers injured, and police said they detained 46 protesters.
Yoon earlier resisted efforts by investigative authorities to question or detain him. He then was apprehended on Jan. 15 in a massive law enforcement operation at his presidential compound.
Leading Yoon’s investigation was the Corruption Investigation Office for High-Ranking Officials, but since his detainment Yoon has refused to attend CIO’s questioning, saying it has no legal authority to investigate rebellion allegations. The CIO has said it can investigate Yoon’s rebellion allegation as it’s related to his abuse of power and other allegations.
Yoon has presidential immunity from most criminal prosecutions, but the privilege does not extend to allegations of rebellion or treason.
The CIO handed over Yoon’s case to the Seoul prosecutors’ office Friday and asked it to indict him on rebellion, abuse of power and obstruction of the National Assembly. By law in South Korea, the leader of a rebellion can face life in prison or the death penalty.
In a statement Saturday, Yoon’s defense team urged prosecutors to immediately release Yoon and launch an investigation on the CIO.
Yoon’s defense minister, police chief and several other military commanders have already been arrested over their roles in the martial law decree.
Hyung-jin Kim, The Associated Press